Part I: Introduction
These days, many companies and industries in Singapore are making use of CNC cutting services to fulfil industrial needs as well as artistic applications such as etching and laser cutting of acrylic pieces for feature walls.
Computer Numerical Cutting, also known as CNC cutting is a manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed computer software to dictate the movement of factory tools and machinery. The CNC software is used to control a wide range of complex types of machinery such as grinders, lathes, and milling machines. In addition, the use of CNC machining has helped many cutting companies perform three-dimensional cutting tasks and jobs, all with just a single set of prompts. Unlike traditional cutting methods, CNC cutting does not require live operators to prompt and guide the commands of machining tools such as levers, buttons, and wheels.
Laser cutting, on the other hand, uses a high-power laser directed through optics and CNC onto the material. Typically, a motion control system is used to follow a CNC or preparatory code (G-code) of the pattern that is to be cut onto the material. From there, the focused laser beam burns, melts, vapourises, or is blown away by a jet of hot gas to give the finished product.
A history of laser cutting
Aside from cutting, laser cut is also used for many processes in Singapore such as engraving, marking, and drilling. As such, many of the laser-based services in the past were fairly entwined, with the first working laser dating back to 1960. From there, many people realised the potential of laser beams – they were able to deliver many end-products with just a narrow beam of light on a single wavelength.

Both laser and CNC cutting are now two of the most commonly used manufacturing processes across the world. These cutting services are used in the engineering, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and most recently, the medical industry. Laser cutting services in the medical industry involve creating life-saving and intricate medical devices. One main advantage of using laser cutting technology is that precision is now easier to achieve whilst still maintaining its affordability.
Part II: Understanding the laser cutting process
The laser beam used in laser cutting is created by the stimulation of lasing materials through electrical discharges or lamps inside a closed container. This is then amplified by reflecting it internally using a partial mirror until its energy is sufficient for it to escape as a stream of coherent monochromatic light. Usually, this light is focused on the work area through the use of mirrors or fibre optics directing the beam. This light then passes through a pair of lenses which further intensifies it.
At its narrowest point, a laser beam can be as thin as 0.0125 inches or 0.32mm in diameter, with kerf widths as small as 0.004 inches, depending on the material thickness. Most of the time, a piercing process is used when the laser needs to start anywhere except the edge of the material. The piercing process uses high-power pulsed lasers to make a hole in the material – burning through a stainless steel or acrylic sheet.
Laser-cut machines can be classified into three main types, with each one offering a continuous wavelength to serve a range of purposes.
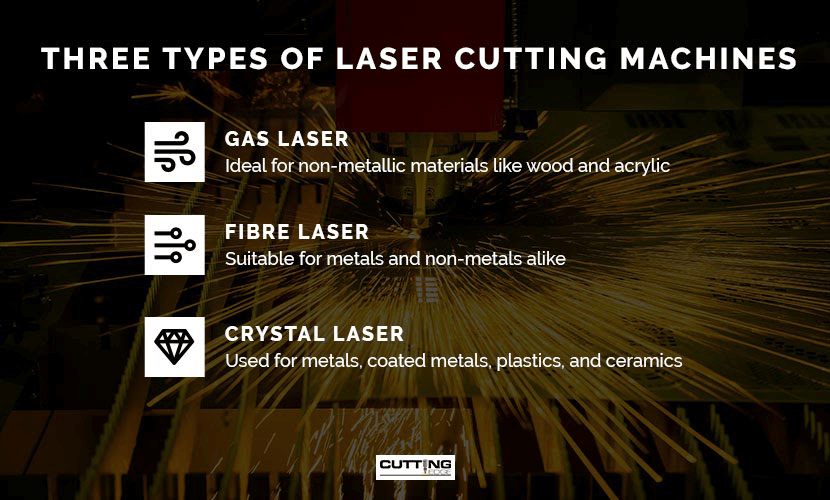
1.Gas Lasers
The common medium used for gas lasers is carbon dioxide (CO2). Most of these lasers are pumped by an electric discharge, however, some designs may require the use of Radio Frequency (RF) waves, photons, and also electron beams (e-beams). CO2 lasers produce invisible light, skewing towards the far infrared range of the light spectrum.
A CO2 laser runs electricity through a tube filled with gas mixture to produce light beams. These tubes contain mirrors on each end, with one of the mirrors being fully reflective, while the other is partial and enables some light to pass through. The gas mixture usually consists of carbon dioxide, hydrogen, helium, and nitrogen.
While typical CO2 laser machines range between 25 to 100 watts in power, industrial laser cut machines can go up to multiple Kilowatts. Gas lasers are ideal for CNC industrial services involving woodcutting, or other laser cutting processes using acrylic. While CO2 lasers are ideal for non-metallic materials such as wood and acrylic, they can also cut through thin sheets of aluminium as well as other non-ferrous metals in processes such as metal engraving.
The other gas that is commonly used for cutting mild and carbon steel is oxygen. Oxygen is most often referred to as cutting gas.
During the process of cutting with oxygen, the metal is burned and vapourised after being heated up to ignition temperature by the laser beam. The reaction between the oxygen and the metal creates additional energy in the form of heat to support the cutting process. The liquid iron oxide has a very low viscosity and is removed from the cut by the sheer force of the oxygen jet.
You can increase the pressure of the oxygen to improve the melt-shear removal process. However, as the increase is not limited by the cooling effect caused by the gas, it can result in bad cuts with significant dross, or no cut at all.
The maximum oxygen pressure is primarily dependent on the material thickness. Usually, thin sheets of 2 or 3mm make use of the oxygen pressure to cut through the material. On the other hand, thicker metal sheets over 20mm use lesser oxygen pressure and more combustion instead.
2.Fibre Lasers
Since their introduction, fibre lasers have revolutionised the laser cutting industry with their speed and wavelength. As mentioned earlier, CO2 lasers are unable to cut through non-ferrous metals such as brass and copper due to their properties and optical reflectivity.
Fibre lasers are part of the solid-state laser group and make use of the seed laser. Through this process, the beams of fibre lasers are amplified using specially designed glass fibres-derived energy from pump diodes.
Fibre lasers tend to be maintenance-free, with a longer service life as compared to other laser machines. Not only can fibre lasers produce strong and stable beams, but they can also manage intensities of a hundred times higher than that of CO2 lasers at the same amount of average power. Unlike CO2 lasers, fibre lasers can be in continuous beam, quasi-, or pulsed settings to produce different functionalities. This also makes them suitable for metal marking processes such as metal engraving. Aside from metals, fibre lasers are also versatile and can be used on alloys, non-metals such as wood, and acrylic.
3.Crystal Lasers
The crystal laser cutting process makes use of two types of crystals. – nd:YAG also known as neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet and nd:YVO, short for neodymium-doped yttrium ortho-vanadate. Of the two, nd:YVO is more commonly used.
These lasers have a smaller wavelength as compared to CO2 lasers, allowing them to have higher intensities to cut through thicker materials. Since they run on higher power intensities, they tend to be more susceptible to wear and tear, thus having a shorter life expectancy.
When comparing between the two types of crystal cut lasers, Nd:YVO exhibits a higher pump absorption and gain, allowing for a broader wavelength range. In terms of continuous operation, Nd:YVO is able to achieve similar results as Nd:YAG. The main difference between the two lasers is that the pulse energies produced by Nd:YVO lasers are not as high as ND:YAG, with laser life lasting for shorter periods of time.
Sharing the same wavelength as fibre lasers at 1.064mm, crystal lasers are also suitable for laser engraving services on materials like metals and plastics. They are also able to cut through various materials such as metals, coated metals, plastics, and even ceramics. However, unlike fibre lasers, crystal ones have relatively expensive pump diodes that need to be replaced after 8,000 to 15,000 laser hours, making them less favourable.
Now that you understand the types of laser cutting machines being used in the industry, let us move on to the various laser cutting methods used in different situations. By knowing the commonly used methods of laser cutting, you can determine the cutting plan that is ideal for meeting your needs.
1.Flame cutting

In the flame cutting process, oxygen is used as the main cutting gas. The oxygen is blown into the kerf at a pressure of up to 6 bar, allowing the heated metal to react with the oxygen. This causes the metal to burn and oxidise. Furthermore, this chemical reaction also releases large amounts of energy, supplementing the laser beam. Because of its ability to cut at high speeds, flame-cutting can handle jobs involving thick plates such as mild steel.
2.Fusion cutting
Laser fusion cutting makes use of inert gases such as nitrogen or argon. The gas is blown molten material out of the kerf at pressures up to 20 bar. By using inert gases, they are able to cool the material whilst preventing oxidation from happening at the cutting edge. This CNC cutting method is recommended for thin sheets, or in situations where the finished workpieces must fulfil high visual requirements without the need for further processing.
3.Remote cutting
Remote cutting uses a high-intensity laser beam to partially evaporate the material, allowing thin sheets to be cut without the need for an assist gas. Through this process, the laser evaporates each layer of the material, creating a very thin cutting gap. This method of cutting is ideal for thin and sensitive material, as well as offers unique solutions for processing a wide range of different composite materials.
Laser cutting uses speed and precision to manufacture designed products at an affordable rate. Even though this process requires a piece to be cut on flat material like a sheet of metal, 3D objects can also be created with the help of equipment and tools designed with laser cutters. As laser cutting machines require you to follow specific design guidelines in order to meet the precision and quality requirements, here are some tips to help you get started on your design process.

1.Use software that support vector files
Most laser cut services in Singapore require the designs to be sent in vector files. Hence you can use software such as Adobe Illustrator or Inkscape to create file types like .ai, .dxf, .eps, .step. It is recommended for you to check with the laser cutting company the file formats they support.
2. Scale and submit the design
Before sending your final artwork in, you need to ensure the design is to scale. For instance, if your piece is meant to be 15-in.squared, then it should be scaled to that exact size for the machine to achieve the right proportions. In addition, you also need to remember to remove any notes, comments, gridlines, as well as borders unrelated to the design files before submission.
As some designs may be complex and have overlapping artwork, it is important to integral for you to omit these lines when sending the final file to the laser cutting company. This prevents the laser cutter from cutting on any lines in your design and causing damage, as well as production delays.
3. Don’t send multiple files of the same design
You should only send only one of each piece if you plan on having more than one cut from the same material. Instead, you can just let the laser cutting company know how many multiples are needed. A reliable company such as Cutting Edge will be able to plan out how the shapes should be arranged on the cuts and keep the material to a minimum. By crowding your design with multiple copies of the same image, you may end up complicating the cutting process and potentially incur extra costs.
4. Connect your design
A common mistake often made by many people looking to cut out a design with words, is that they fail to bridge their design and text in the file. Other than holes, all shapes will be lost if they are not connected to the primary material in the design file. Hence, it is recommended for you to add a bridge so that the laser can make a clean cut whilst keeping the entire design together. Furthermore, laser cutters are also unable to process active text boxes (to tell if it is an active text box, you can hover your cursor over the text in your design. If it shows an editing bar, this means that your text is active). Instead, you should turn the text box into shapes for ease of processing by the laser cutter.
You should always consult the cutting company that you are engaging in when in doubt during your design process. A good and reliable cutting company is able to properly advise you on the design aspects, as well as the materials and costs so that you can enjoy a hassle-free experience.
Part III: The benefits of laser cutting and how to differentiate it from the rest
Before the introduction of laser and CNC cutting machines, saw cutting was the standard method used to fabricate materials. Two of the most common sawing methods for fabrication were the scroll saw and band saw.
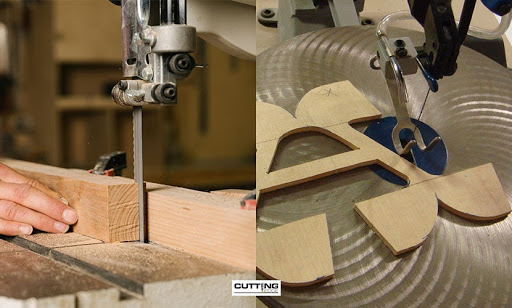
The scroll saw is a hands-free sawing method where a technician pedals to move it up and down, creating speciality cuts as well as crafting designs. On the other hand, band saws do not move up and down as scroll saws do. Instead, the blade is thin with specialised teeth, and is attached in a stationary position and moving wheels to facilitate cutting movement. Saw cutting is known to be a good fit for a wide variety of projects such as decorative detailing and metal cutting work for industrial projects.
As mentioned above, laser cutting is a fast and efficient method of material fabrication for both simple cuts and detailed work. A lot of businesses rely on laser and CNC cutting to create products like sculptures, interior designs such as walls or acoustic panels, metal engraving, signboards, and more. Laser cutting also gives you the option to choose between two and three-dimensional designs.

The following features of laser cutting have made it an ideal fabrication solution for many projects:
1. Precision – Laser cutting offers a high level of precision and accuracy for detailed work. Because of its precision level, it is able to achieve sizes and designs that traditional saw cutting methods cannot. This in turn results in fewer errors, and thus incur lesser costs over time. Due to its higher level of precision, it is able to adhere to strict requirements especially when it comes to cutting out parts and designs for computer companies.
2. Versatile programming options – One of the most significant benefits of using a laser cutter for your project is its versatile programmes. This allows you to send your designs in, and the technician will input the required information such as the design specs and dimension into the computer system. From there the laser machine will craft and cut out the design without further manual work.
3. Hands-free procedure – The laser cutting process uses computerised systems thus minimising the risks for contamination of sensitive materials. Also, since the machine separates the finished product from the leftover scraps, it eliminates the need for post-processing. Hands-free cutting procedures also mean the technician can work on multiple projects concurrently, allowing you to save more time and money, especially when it comes to a large-scale project.
What is the difference between laser cutting and the other processes?
For some, the terminology can come across as a little confusing, especially when it seems like laser marking, cutting, and engraving are similar processes using laser technology. However, each process is different, and thus may not be able to suit your project.
To decide between each process, you need to identify the nature of your project as well as the materials you are working with.

Laser engraving is one of the most commonly used methods to mark products and materials. During this process, the material is removed to create depth, resulting in a more permanent result. Metals and plastics are often the materials of choice when it comes to laser engraving. However, in some cases, removing the surface material may lead to oxidation and increased risks of rusting to create an undesirable effect.
Laser engraving is perfect for labelling, engraving of serial numbers on small parts, detailed logos, inscriptions, and even photographs of you or your loved ones.
Laser marking becomes the ideal choice if you do not wish to damage the longevity or integrity and appearance of your product. In this process, laser marking does not cut into the surface of the material, enabling it to stay intact. Thus, preventing rust and oxidation from taking place. Laser marking is ideal for medical equipment such as surgical tools.
Part IV: Conclusion
In recent years, laser and CNC cutting services have become one of the most sought-after processes by businesses and designers alike. From cutting out large pieces of materials to bringing digital designs to life, laser cutters are handy tools for prototyping and manufacturing.
Working with a professional fabrication company in Singapore offering laser cutting and CNC cutting services is the best way to achieve quality results. It also eliminates the need to invest in costly machinery or specialised training. Aside from having trained technicians to work with a variety of materials, a licensed laser cutting company also maintains strict quality standards to produce optimal levels of performance.
Cutting Edge is a professional company that specialises in CNC cutting, laser cutting, engraving services, as well as the production of acoustic walls. Here, we maintain strict quality standards so you know you are getting the best. Share with us your project details and let us help you bring your designs to life.